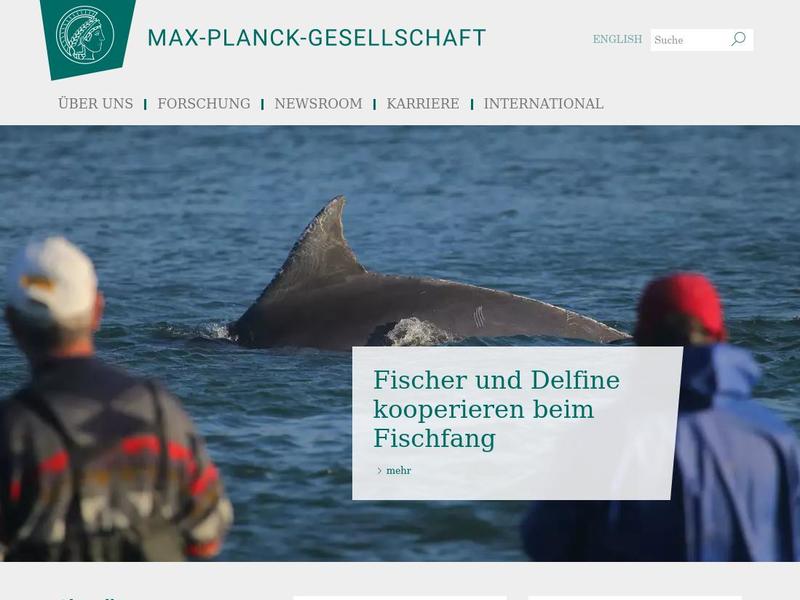
Max-Planck-Princeton partnership in fusion research confirmed https://www.mpg.de/11805837/max-planck-princeton-partnership-in-fusion-research-confirmed
The scientific performance of Max-Planck-Princeton Center for Plasma Physics, established in 2012 by the Max Planck Society and Princeton University, USA, has been evaluated and awarded top grade. The Max Planck Society has now decided to continue its support for another two to maximum five years with 250,000 euros annually. The center’s objective is to link up the hitherto less coordinated research on fusion, laboratory and space plasmas and utilise synergies.
Turbulence in solar wind plasma.